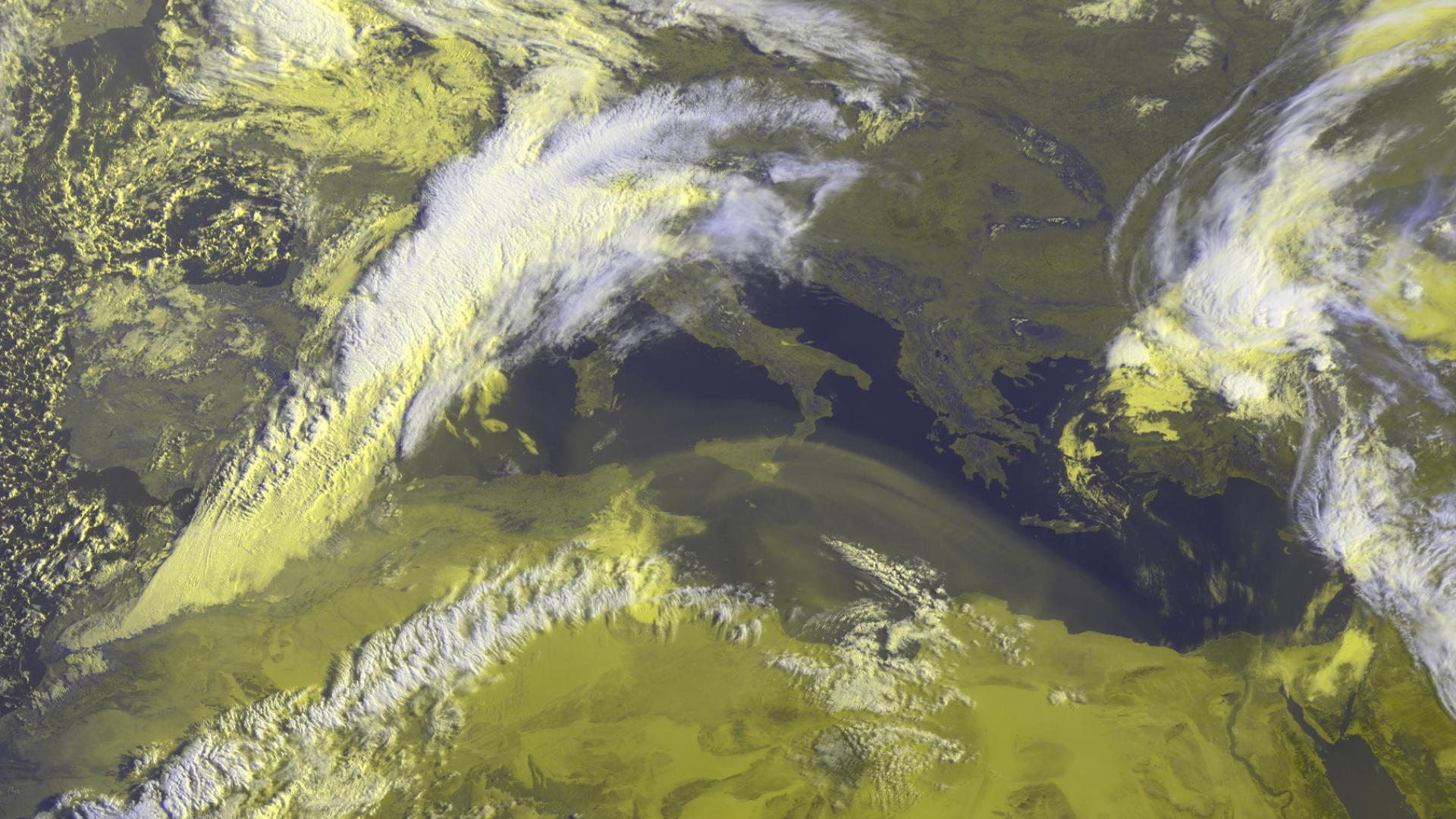
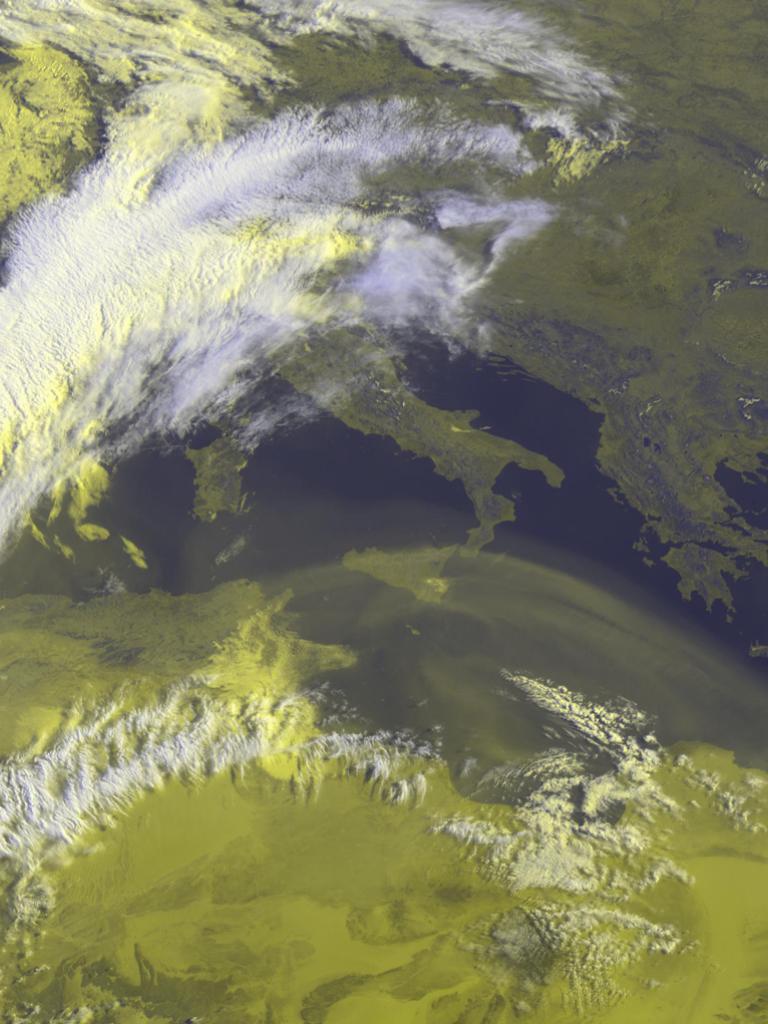
Desert dust particles are lifted into the atmosphere by gusts of surface wind and can be transported and deposited thousands of kilometres away.
When Saharan dust travels over populated areas, it can reduce air quality and impact health by causing respiratory problems and cause flight delays. Over the oceans, dust can act as a fertiliser, stimulating blooms of tiny marine plants (phytoplankton) that are the basis for the marine food chain.
The image was captured by the EUMETSAT’s Meteosat-11 weather satellite. The Meteosat satellites are a key part of the global ring of geostationary weather satellites and observe the Earth over Europe, Africa and the Indian Ocean. See their current view from our Earth view stream.