22 January 2025
22 March 2023
CO2M will be the main satellite component of a new European CO2 monitoring and verification support capacity (CO2MVS) for monitoring global anthropogenic (human-made) CO2 and CH4 emissions. CO2MVS is being developed as part of the EU’s Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service.
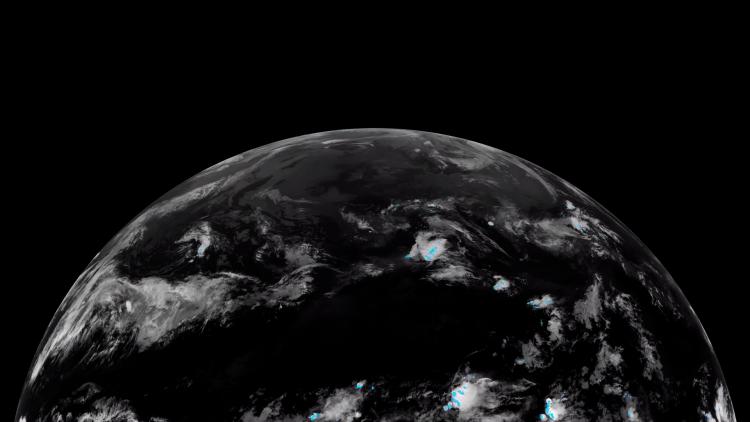
Monitoring global greenhouse gases
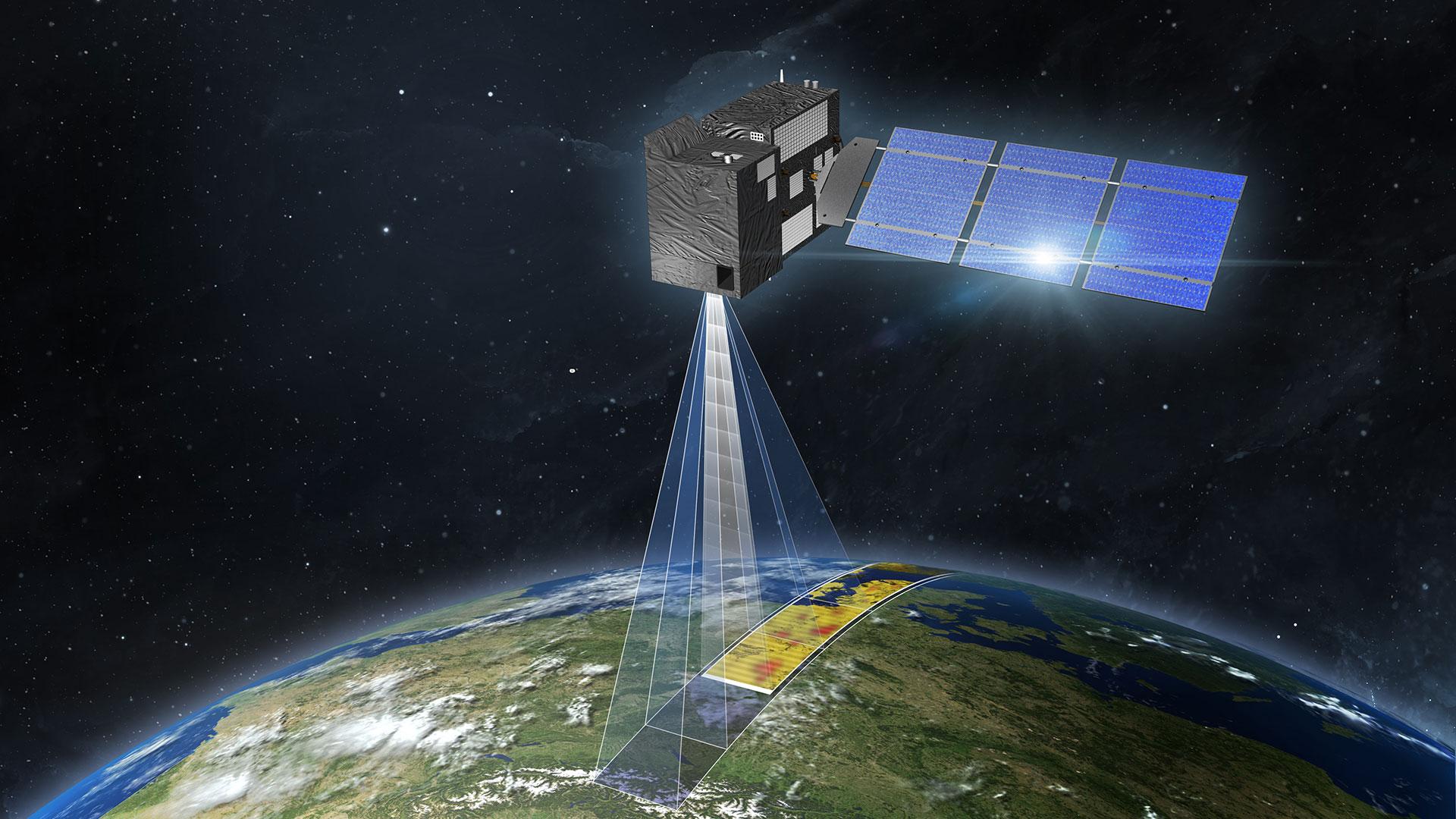
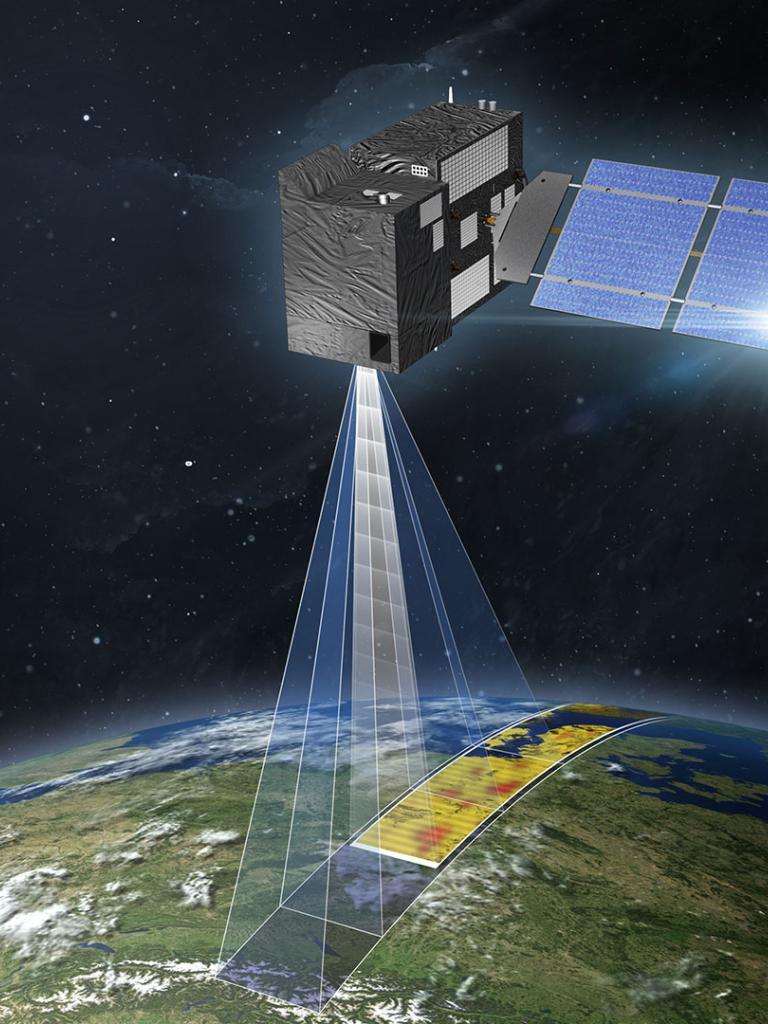
The first of the two CO2M platforms will be delivered to the launch service by end of 2026 and will operate, after launch, for a minimum of 7.5 years. Both satellites will carry a near-infrared and shortwave-infrared spectrometer (CO2I) to measure atmospheric carbon dioxide and methane at high spatial resolution.
The greenhouse gas observations gathered by CO2M will be combined with ground-based measurements and modelling at the CO2MVS, to distinguish anthropogenic (human-made) emissions of CO2 and CH4 from natural sources, such as plants and animals.
The anthropogenic emissions data will then be used as a transparent and independent data source to follow progress with national CO2 reduction commitments that were agreed in the Paris Agreement on Climate.
In addition to greenhouse gases, the CO2M satellite will also monitor cloud cover, aerosols and sun-induced fluorescence (SIF). SIF monitoring is a new capability that will lead to better estimates of natural CO2 sources from vegetation during the growing season. This will help in the process of disentangling anthropogenic CO2 emissions from natural sources.
“EUMETSAT will operate the CO2M satellites and receive, process and disseminate their data, which will be crucial for monitoring carbon emission reduction efforts globally, in line with the Paris Agreement.” Phil Evans, EUMETSAT Director-General
CO2M will carry three main instruments:
Combined CO2 and NO2 Imaging Spectrometer
The combined CO2 and NO2 Imaging Spectrometer (CO2I/NO2I) will measure carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) concentrations in the atmosphere. It has a spatial resolution of 4 km.
Multi-Angle Polarimeter (MAP)
Multi-Angle Polarimeter (MAP): This instrument will measure the polarization of light reflected by the Earth's atmosphere. This information will be used to retrieve aerosol properties, which are important for correcting CO2 measurements.
Cloud Imager (CLIM)
Cloud Imager (CLIM): This instrument will provide high-resolution images of clouds. This information will be used to mask out clouds from CO2 retrievals.
In general, CO2M will also help scientists to better understand the carbon cycle and how human activities are having an impact on it. This knowledge will be essential for developing effective climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies.
International cooperation
The CO2M mission is funded by the Copernicus Programme. EUMETSAT’s role is to develop a significant part of the CO2M ground segment and operate the satellite and process CO2M products, as part of the Copernicus Third Party Program. ESA is developing the satellites and parts of the overall CO2M ground segment.